How do muscles work?
Submission One
I’m finding out how muscles work in regards to what makes them move, but which muscles groups am I talking about?
They are:
They are:
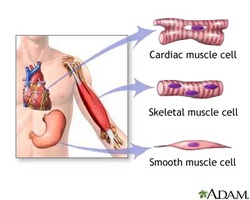
http://www.umm.edu/graphics/images/en/19917.jpg
Skeletal muscle - These are voluntary muscles, so they can be consciously controlled by an animal. These muscles are the largest muscles in a vertebrate’s body; they are connected to the bones by either sheets of tissue or by tendons. When this voluntary muscle contracts it makes a part of the skeleton move.
- Cardiac muscle - This is a kind of involuntary muscle, in this case is the muscular tissue of the heart, which means it contracts and relaxes automatically and has an inbuilt rhythm. The contractions of these muscles pump blood through the body.
- Smooth muscle - These are also involuntary muscles, meaning they are not under an animal’s direct control. The involuntary muscle contracts automatically when triggered by the autonomic nervous system or by chemicals such as hormones, they are usually connected to soft parts of the body, and change the shape of an organ or other body part when they contract.
I wanted to focus on the skeletal muscles as these are the main muscles that produce movement of the skeleton.
Muscles can pull, but they can’t push. They are often arranged in pairs or groups so that when one muscle contracts, the other relaxes.
For example in the following images:
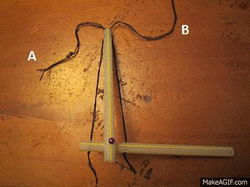
Please click on image for animation (Photo taken by Tasmin)
String A = Triceps, String B = Bicep, Straws represent the Humerus, Radius and Ulna.
This is showing that if you pull string A the arm is raised by the biceps contracting which means the bicep is flexing and the triceps are extended.
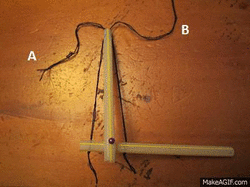
Please click on image for animation (Photo taken by Tasmin)
In this Second picture, this is showing the opposite. When you pull string B the arm is lowered, the triceps has contracted which means it is now flexing and the bicep will be extended. As these muscles are attached to the skeleton this produces the skeleton to move.
Muscles are made of cells called muscles fibres. These cells are several centimetres long, and can shorten, or contract. An individual muscle often contains millions of fibres and their combined force gives the muscle strength. Muscle fibres obtain energy they need to contract from respiration. Most muscle fibres contract when they are triggered by nerves. The muscles contract when fibres shorten, and relaxes when they return to their original length.
~Source: Dictionary of Nature by David Burnie ~
In conclusion I've learnt that skeletal muscles are the reason that body parts are able to move from contracting.
Sources:
- http://library.thinkquest.org/5777/mus3.htm
- http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/life/human-biology/muscle.htm
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jxk5tFiGVSE
- Dictionary of Nature by David Burnie
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed